Stock Portfolio Organizer
The ultimate porfolio management solution.
WiseTrader Toolbox
#1 Selling Amibroker Plugin featuring:
Trigonometric Fit for Amibroker (AFL)
AR_Prediction.afl compute AR (Auto-Regressive) model from the data.
Burg method is called too Maximum Likelihood, Maximum Entropy Method (MEM),
Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis (MESA). All are the same. Yule-Walker method is based on the Autocorellation of the data and by minimising the Least Square error between model and data.
Purpose of AR modeling are to obtain a simple model to describe data.
From this model we can for two main application :
- Calculate future data (make prediction). It is possible because the model is
described by a mathematical expression.
- Make spectral analysis to exctract main cycle from the data. Spectral Analysis is
more powerfull this way than classic FFT for short horizon data and for spectrum which have sharp frequency (cyclic signal)
Screenshots
Similar Indicators / Formulas
Indicator / Formula
// ******************************************************************************************
// *
// * Trigonometric Fit Based on :
// * - AR MODELING (Burg AND Yule-Walker method are implemented) for frequency estimation
// * - Generalized Least Square Error to compute Amplitudes and Phases
// * (because AR estimate of the amplitudes on the spectrum are bad)
// *
// *
// * Main features :
// * - Trigonometric Fit : find up to 10 or more dominant cycles from the data, with amplitudes and phases
// * - Prediction : calculate future datas based on past data, past volume and past low/high
// * - Spectral analysis : compute sharp and clean spectrum of the data and plot it in Decibels
// *
// *
// * Native AFL for maximum speed without needed external dll
// * Many criterions for auto order selection : FPE, AIC, MDL, CAT, CIC ...
// * + 1 necessary VBS Script to compute Amplitudes and Phases for TrigFit (because of matrix notation)
// * + 2 optionnal VBS Scripts (one for experimentation about rounding, the other for PolyFit detrending)
// *
// *
// * Use and modify it freely. v0.05, tomy_frenchy, tom_borgo@hotmail.com, mich. 12/2006.
// * Thanks to Fred for PolyFit function AFL and Gaussian Elimination VBS
// *
// ******************************************************************************************
// ******************************************************************************************
// *
// * DESCRITION
// *
// * AR_Prediction.afl compute AR (Auto-Regressive) model from the data.
// * Burg method is called too Maximum Likelihood, Maximum Entropy Method (MEM),
// * Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis (MESA). All are the same.
// * Yule-Walker method is based on the Autocorellation of the data and by minimising
// * the Least Square error between model and data.
// *
// * Purpose of AR modeling are to obtain a simple model to describe data.
// * From this model we can for two main application :
// * - Calculate future data (make prediction). It is possible because the model is
// * described by a mathematical expression.
// * - Make spectral analysis to exctract main cycle from the data. Spectral Analysis is
// * more powerfull this way than classic FFT for short horizon data and for spectrum wich
// * have sharp frequency (cyclic signal)
// *
// *
// * MAIN FUNCTION :
// * 1- AR_Burg: to compute AR Burg model
// * 2- AR_YuleWalker: to compute AR Yule Walker model
// * 3- AR_Predict: to predict future data based on the computed AR model
// * 4- AR_Freq: to compute the spectrum from the computed AR model
// * 5- AR_Sin: to find main frequency in the computed spectrum (dominant cycles from the data)
// *
// *
// * ALL THE CODE IS COMMENTED SO YOU CAN FIND PARAMETERS FOR THE FUNCTION IN THE DEMO SECTION AT THE END OF THE FILE.
// * All the source is commented, so you can learn a lot from it.
// * There are many sources paper on the net about the subject.
// *
// *
// ******************************************************************************************
// ******************************************************************************************
// *
// * PARAMETERS
// *
// *
// *
// * Main parameters for AR modeling :
// *
// *
// * Price field = Data to predict
// * AR Model = Burg model or Yule-Yalker model
// * Length to look back = Horizon used on the data to compute the model
// * Order AR = Order wanted for the AR model
// * Number of bar to predict = Length prediction
// * Auto AR order = Find automatically the best order
// * Auto AR criterion = Criterion to use for Auto AR order
// * FPE: Final Prediction Error (classic old one)
// * AIC: Akaine Information Criterion (classic less old one)
// * MDL: Minimum Description Length
// * CAT: Criterion Autoregressive Transfer
// * CIC: Combined Information Criterion (good one)
// * Mixed: An upper averaging from all those criterion (best, recommended)
// * Burg: Hamming Window = If Hamming Window is applyed during model computation (only Burg model)
// * Burg: Double Precision = If Double Precision is used to compute the model (only Burg model)
// * Y-W: Biased = If Autocorrelation estimator should be biased (Yes) or not-biased (No) (only Yule-Walker model)
// *
// *
// *
// * Pre-Processing begore modeling AR model :
// *
// *
// * Intraday EOD GAP Filter = For intraday data, first data of the day is same than last data of yesterday day
// *
// *
// * Periods T3 = Periods for Tillson's T3 filter (high order low pass denoiser)
// * Slope T3 = Slope for Tillson's T3 filter (0.7 to 0.83 for usual value) (Higher value mean more dynamic filter)
// *
// *
// * Detrending method = Method to use to detrend the data
// * None: no detrending is done
// * Log10: log10(data) detrending is done (usefull for trend wich increase with time)
// * Derivation: differentiation one by one from the data (prefered method because is sure to kill the linear trend)
// * Linear Regression: substract linear regression from the data (good method too if fitting is ok)
// * PolyFit: substract n-th order polynomial regression from the data (order 3 can give nice result)
// * PolyFit Order = Order for the PolyFit detrending method (usefull just if you choose this method of detrending)
// *
// *
// * Center data = Remove the bias in the data (substract the mean).
// * AR modeling NEED NOT BIASED data, so this sould be always left on "Yes".
// *
// *
// * Normalize = Scale data between [-1;1] (usefull for better computation because less rounding error)
// *
// *
// * Volume HL weight on data = Multiply data by a factor computed from volume and high/low information from the data
// * !!! This is experimental feature !!!
// * Strength Volume = Strength of volume weighting
// * Strength Fractal = Strength of High/Low (Fractal) weighting
// * Periods Fract (even) = Periods to compute the fractal factor (an even period is needed)
// * Scale Final Weights = Final dynamic of the weights (high value increase difference between low weight and high weight)
// * Translate Final Weights = Final strength of the weights (high value bring all the weights near their maximum)
// * Scale / Translate is based on Inverse Fisher Transform and work like a limiter/compressor of the weights
// *
// *
// * Time weight on data = Apply time windowing on data so more recent data are more weighted than old data to compute the AR model
// * Weighting Time Window = Choose the strength of the weights
// * Log: natural logarithm, small time weigthing on the data
// * Ramp: a ramp, linear time weigthing on the data
// * Exp: exponential, strong time weigthing on the data
// *
// *
// *
// * Post-Processing before plotting predicted data :
// *
// * Retrending method = Choose if trend should be added back to predicted data
// * Trend is automatically added back for "Log10" and "Derivation" methods,
// * so data stay in good scale
// *
// * Color PolyFit = Color to plot the curve from "PolyFit" detrending method
// * Color PolyFit = Color to plot the line from "Linear Regression" detrending method
// *
// *
// ******************************************************************************************
EnableScript("VBScript");
<%
function TrigFit_amplitudesphases(data, BegBar, EndBar, frequency, nb_frequency)
'Compute 2*nb_frequency Amplitudes for given frequency based on Generalized Least Square Error
Dim W()
Dim x()
Dim x_temp
Dim x_final
Dim b
Dim Coeff
Dim result
LongBar = EndBar - BegBar + 1
nb_variable = 2 * nb_frequency
ReDim W(nb_variable)
ReDim x(10000, nb_variable + 1)
ReDim x_temp(10000, nb_variable + 1)
ReDim x_final(nb_variable, nb_variable + 1)
ReDim b(nb_variable, nb_variable)
ReDim Coeff(nb_variable)
ReDim result(nb_variable)
pi2 = Atn(1) * 8
'Compute the pulsation
for i = 1 To nb_frequency
W(i) = pi2 / frequency(i - 1)
Next
'Compute original matrix
for i = BegBar To EndBar
for j = 1 To nb_variable - 1 Step 2
x(i, j) = cos(W((j + 1) / 2) * i)
Next
for j = 2 To nb_variable Step 2
x(i, j) = sin(W(j / 2) * i)
Next
Next
for i = BegBar To EndBar
x(i, nb_variable + 1) = data(i)
Next
'Compute Least Square matrix
for n = 1 To nb_variable
for i = BegBar To EndBar
for j = 1 To nb_variable + 1
x_temp(i, j) = x(i, j) * x(i, n)
Next
Next
for j = 1 To nb_variable + 1
Sum = 0
for i = BegBar To EndBar
Sum = Sum + x_temp(i, j)
Next
x_final(n, j) = Sum
Next
Next
'Prepare for Gaussian Elimination
for i = 1 To nb_variable
for j = 1 To nb_variable
b(i, j) = x_final(i, j)
Next
Next
for i = 1 To nb_variable
W(i) = x_final(i, nb_variable + 1)
Next
'Gaussian Elimination
n = nb_variable
n1 = n - 1
for i = 1 To n1
big = CDbl(abs(b(i, i)))
q = i
i1 = i + 1
for j = i1 To n
ab = CDbl(abs(b(j, i)))
if (ab >= big) Then
big = ab
q = j
End if
Next
if (big <> 0) Then
if (q <> i) Then
for j = 1 To n
temp = CDbl(b(q, j))
b(q, j) = b(i, j)
b(i, j) = temp
Next
temp = W(i)
W(i) = W(q)
W(q) = temp
End if
End if
for j = i1 To n
t = CDbl(b(j, i) / b(i, i))
for k = i1 To n
b(j, k) = b(j, k) - t * b(i, k)
Next
W(j) = W(j) - t * W(i)
Next
Next
if (b(n, n) <> 0) Then
Coeff(n) = W(n) / b(n, n)
i = n - 1
while i > 0
SumY = CDbl(0)
i1 = i + 1
for j = i1 To n
SumY = SumY + b(i, j) * Coeff(j)
Next
Coeff(i) = (W(i) - SumY) / b(i, i)
i = i - 1
Wend
'TrigFit_amplitudes = Coeff
End if
'Compute composite amplitudes AND phases
for i = 1 To nb_variable Step 2
result(i) = Sqr(Coeff(i) ^ 2 + Coeff(i + 1) ^ 2)
if (Coeff(i + 1) = 0) Then 'Denominator is equal to zero
if (Coeff(i) >= 0) Then 'Positive numerator
result(i + 1) = pi2 / 4
End if
if (Coeff(i) < 0) Then 'Negative numerator
result(i + 1) = -pi2 / 4
End if
ElseIf (Coeff(i + 1) > 0) Then 'Denominator is positive
result(i + 1) = Atn(Coeff(i) / Coeff(i + 1))
ElseIf (Coeff(i + 1) < 0) Then 'Denominator is negative
result(i + 1) = pi2 / 2 + Atn(Coeff(i) / Coeff(i + 1))
End if
Next
TrigFit_amplitudesphases = result
End function
' Called by ARG_Burg AFL funct. to compute Ki in Double Precision
function Compute_KI(f, b, W, i, LongBar)
n = LongBar - 1
for j = i to n
Num = Num + cDBL(W(j))*( cDBL(f(j))*cDBL(b(j-1)) )
Den = Den + cDBL(W(j))*( cDBL(f(j))^2 + cDBL(b(j-1))^2 )
next
KI = 2*Num/Den
Compute_KI = KI
end function
function Gaussian_Elimination (GE_Order, GE_N, GE_SumXn, GE_SumYXn)
Dim b(10, 10)
Dim w(10)
Dim Coeff(10)
for i = 1 To 10
Coeff(i) = 0
next
n = GE_Order + 1
for i = 1 to n
for j = 1 to n
if i = 1 AND j = 1 then
b(i, j) = cDBL(GE_N)
else
b(i, j) = cDbl(GE_SumXn(i + j - 2))
end if
next
w(i) = cDbl(GE_SumYXn(i))
next
n1 = n - 1
for i = 1 to n1
big = cDbl(abs(b(i, i)))
q = i
i1 = i + 1
for j = i1 to n
ab = cDbl(abs(b(j, i)))
if (ab >= big) then
big = ab
q = j
end if
next
if (big <> 0.0) then
if (q <> i) then
for j = 1 to n
Temp = cDbl(b(q, j))
b(q, j) = b(i, j)
b(i, j) = Temp
next
Temp = w(i)
w(i) = w(q)
w(q) = Temp
end if
end if
for j = i1 to n
t = cDbl(b(j, i) / b(i, i))
for k = i1 to n
b(j, k) = b(j, k) - t * b(i, k)
next
w(j) = w(j) - t * w(i)
next
next
if (b(n, n) <> 0.0) then
Coeff(n) = w(n) / b(n, n)
i = n - 1
while i > 0
SumY = cDbl(0)
i1 = i + 1
for j = i1 to n
SumY = SumY + b(i, j) * Coeff(j)
next
Coeff(i) = (w(i) - SumY) / b(i, i)
i = i - 1
wend
Gaussian_Elimination = Coeff
end if
end function
%>
function PolyFit(GE_Y, GE_BegBar, GE_EndBar, GE_Order, GE_ExtraB, GE_ExtraF)
{
BI = BarIndex();
GE_N = GE_EndBar - GE_BegBar + 1;
GE_XBegin = -(GE_N - 1) / 2;
GE_X = IIf(BI < GE_BegBar, 0, IIf(BI > GE_EndBar, 0, (GE_XBegin + BI - GE_BegBar)));
GE_X_Max = LastValue(Highest(GE_X));
GE_X = GE_X / GE_X_Max;
X1 = GE_X;
GE_Y = IIf(BI < GE_BegBar, 0, IIf(BI > GE_EndBar, 0, GE_Y));
GE_SumXn = Cum(0);
GE_SumXn[1] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X));
GE_X2 = GE_X * GE_X; GE_SumXn[2] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X2));
GE_X3 = GE_X * GE_X2; GE_SumXn[3] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X3));
GE_X4 = GE_X * GE_X3; GE_SumXn[4] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X4));
GE_X5 = GE_X * GE_X4; GE_SumXn[5] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X5));
GE_X6 = GE_X * GE_X5; GE_SumXn[6] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X6));
GE_X7 = GE_X * GE_X6; GE_SumXn[7] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X7));
GE_X8 = GE_X * GE_X7; GE_SumXn[8] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X8));
GE_X9 = GE_X * GE_X8; GE_SumXn[9] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X9));
GE_X10 = GE_X * GE_X9; GE_SumXn[10] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X10));
GE_X11 = GE_X * GE_X10; GE_SumXn[11] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X11));
GE_X12 = GE_X * GE_X11; GE_SumXn[12] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X12));
GE_X13 = GE_X * GE_X12; GE_SumXn[13] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X13));
GE_X14 = GE_X * GE_X13; GE_SumXn[14] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X14));
GE_X15 = GE_X * GE_X14; GE_SumXn[15] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X15));
GE_X16 = GE_X * GE_X15; GE_SumXn[16] = LastValue(Cum(GE_X16));
GE_SumYXn = Cum(0);
GE_SumYXn[1] = LastValue(Cum(GE_Y));
GE_YX = GE_Y * GE_X; GE_SumYXn[2] = LastValue(Cum(GE_YX));
GE_YX2 = GE_YX * GE_X; GE_SumYXn[3] = LastValue(Cum(GE_YX2));
GE_YX3 = GE_YX2 * GE_X; GE_SumYXn[4] = LastValue(Cum(GE_YX3));
GE_YX4 = GE_YX3 * GE_X; GE_SumYXn[5] = LastValue(Cum(GE_YX4));
GE_YX5 = GE_YX4 * GE_X; GE_SumYXn[6] = LastValue(Cum(GE_YX5));
GE_YX6 = GE_YX5 * GE_X; GE_SumYXn[7] = LastValue(Cum(GE_YX6));
GE_YX7 = GE_YX6 * GE_X; GE_SumYXn[8] = LastValue(Cum(GE_YX7));
GE_YX8 = GE_YX7 * GE_X; GE_SumYXn[9] = LastValue(Cum(GE_YX8));
GE_Coeff = Cum(0);
GE_VBS = GetScriptObject();
GE_Coeff = GE_VBS.Gaussian_Elimination(GE_Order, GE_N, GE_SumXn, GE_SumYXn);
for (i = 1; i <= GE_Order + 1; i++)
printf(NumToStr(i, 1.0) + " = " + NumToStr(GE_Coeff[i], 1.9) + "\n");
GE_X = IIf(BI < GE_BegBar - GE_ExtraB - GE_ExtraF, 0, IIf(BI > GE_EndBar, 0, (GE_XBegin + BI - GE_BegBar + GE_ExtraF) / GE_X_Max));
GE_X2 = GE_X * GE_X; GE_X3 = GE_X2 * GE_X; GE_X4 = GE_X3 * GE_X; GE_X5 = GE_X4 * GE_X; GE_X6 = GE_X5 * GE_X;
GE_X7 = GE_X6 * GE_X; GE_X8 = GE_X7 * GE_X; GE_X9 = GE_X8 * GE_X; GE_X10 = GE_X9 * GE_X; GE_X11 = GE_X10 * GE_X;
GE_X12 = GE_X11 * GE_X; GE_X13 = GE_X12 * GE_X; GE_X14 = GE_X13 * GE_X; GE_X15 = GE_X14 * GE_X; GE_X16 = GE_X15 * GE_X;
GE_Yn = IIf(BI < GE_BegBar - GE_ExtraB - GE_ExtraF, Null, IIf(BI > GE_EndBar, Null,
GE_Coeff[1] +
GE_Coeff[2] * GE_X + GE_Coeff[3] * GE_X2 + GE_Coeff[4] * GE_X3 + GE_Coeff[5] * GE_X4 + GE_Coeff[6] * GE_X5 +
GE_Coeff[7] * GE_X6 + GE_Coeff[8] * GE_X7 + GE_Coeff[9] * GE_X8));
return GE_Yn;
}
function Time_weighting(data, window, BegBar, EndBar) {
BI = BarIndex();
if (window == "Log") alphatime = log(Cum(1));
if (window == "Ramp") alphatime = Cum(1);
if (window == "Exp") alphatime = exp(Cum(0.01));
alphatime = Ref(alphatime, -BegBar);
alphatime = alphatime - alphatime[BegBar];
alphatime = alphatime / alphatime[EndBar];
alphatime = IIf(BI < BegBar, 0, IIf(BI > EndBar, 0, alphatime));
return alphatime*data;
}
function Volume_HighLow_weighting(data, coef_vol, coefdim, period, scale, translation) {
// Coefficient Volume
highvol = V; highvol = HHV(Median(V, 5), 5000);
nbr_vol = coef_vol*highvol/(1 - coef_vol) + 1;
alpha_vol = V/nbr_vol;
alpha_vol = IIf(alpha_vol > 0.99, 0.99, alpha_vol);
alpha_vol = IIf(alpha_vol < 0.01, 0.01, alpha_vol);
// Coefficient High/Low (Adpated from FRAMA from John Ehlers)
coefdim = coefdim * 2 - 0.01;
N = 2*floor(period/2);
delta1 = HHV(Ref(High, -N/2), N/2) - LLV(Ref(Low, -N/2), N/2);
delta2 = HHV(High, N/2) - LLV(Low, N/2);
delta = HHV(High, N) - LLV(Low, N);
Dimen = log((delta1 + delta2)/delta)/log(2);
alphadim = exp(-coefdim*Dimen);
alphadimnorm = Min(Max(alphadim, 0.01), 0.99);
// Mix Volume and High/Low, and scale them with Inverse Fisher Tansform
alpha = alphadimnorm + alpha_vol;
data_av = scale*(alpha - translation);
alpha = (exp(2*data_av) - 1)/(exp(2*data_av) + 1);
alpha = Min(Max(alpha,0.01),0.99);
return alpha*data;
}
function Filter_GAP_EOD(data) {
time_frame = Minute() - Ref(Minute(), -1);
time_frame = IIf(time_frame < 0, time_frame + 60, time_frame);
time_frame = time_frame[1];
day_begin = 152900 + 100*time_frame;
day_end = 215900;
delta = 0;
timequote = TimeNum();
for (i = 1; i < BarCount; i++) {
if (timequote[i] == Day_begin) delta = data[i] - data[i-1];
data[i] = data[i] - delta;
}
return data;
}
function T3(data, periods, slope) { // High Order Low-Pass filter
e1 = EMA(data, periods);
e2 = EMA(e1, periods);
e3 = EMA(e2, periods);
e4 = EMA(e3, periods);
e5 = EMA(e4, periods);
e6 = EMA(e5, periods);
c1 = -slope*slope*slope;
c2 = 3*slope*slope + 3*slope*slope*slope;
c3 = -6*slope*slope - 3*slope - 3*slope*slope*slope;
c4 = 1 + 3*slope+slope*slope*slope + 3*slope*slope;
result = c1*e6 + c2*e5 + c3*e4 + c4*e3;
return result;
}
function f_centeredT3(data, periods, slope) { // Centered T3 Moving Average
slide = floor(periods/2);
centeredT3 = data;
centeredT3 = Ref(T3(data,periods,slope),slide);
centeredT3 = IIf( IsNan(centeredT3) OR !IsFinite(centeredT3) OR IsNull(centeredT3), data, centeredT3);
return centeredT3;
}
function f_detrend(data, BegBar, EndBar, ExtraF, method_detrend, PF_order) { // Detrend data
BI = BarIndex();
LongBar = EndBar - BegBar + 1 ;
detrended[0] = 0;
if (method_detrend == "Log10") detrended = log10(data);
if (method_detrend == "Derivation") detrended = data - Ref(data, -1);
if (method_detrend == "Linear Regression") {
x = Cum(1); x = Ref(x,-1); x[0] = 0; x = Ref(x, -BegBar);
a = LinRegSlope(data, LongBar); a = a[EndBar];
b = LinRegIntercept(data, LongBar); b = b[EndBar];
y = a*x + b;
global detrending_parameters;
detrending_parameters = y;
y = IIf(BI < BegBar, Null, IIf(BI > EndBar + ExtraF, Null, y));
Plot( y, "Linear Regression", ParamColor( "Color Linear Regression", colorCycle ), ParamStyle("Style") );
detrended = data - y;
}
if (method_detrend == "PolyFit") {
Yn = PolyFit(data, BegBar, EndBar, PF_order, 0, ExtraF);
Yn = Ref(Yn, -ExtraF);
global detrending_parameters;
detrending_parameters = Yn;
Yn = IIf(BI < BegBar, Null, IIf(BI > EndBar + ExtraF, Null, Yn));
Plot( Yn, "PolyFit", ParamColor( "Color PolyFit", colorCycle ), ParamStyle("Style") );
detrended = data - Yn;
}
return detrended;
}
function f_retrend(data, Value_BegBar, BegBar, EndBar, method_detrend) {
BI = BarIndex();
retrended = Null;
if (method_detrend == "Log10") {
retrended = 10^(data);
}
if (method_detrend == "Derivation") {
retrended[BegBar] = Value_BegBar;
for (i = BegBar + 1; i < EndBar + 1; i++) retrended[i] = data[i] + retrended[i-1];
}
if (method_detrend == "Linear Regression") {
retrended = data + detrending_parameters;
}
if (method_detrend == "PolyFit") {
retrended = data + detrending_parameters;
}
return retrended;
}
function durbinlevison(Autocorr, OrderAR, LongBar, AutoOrder, AutoOrder_Criterion) { // for Yule Walker method only
// Initialization
AR_Coeff = 0;
alpha[1] = noise_variance[1] = Autocorr[0];
beta[1] = Autocorr[1];
k[1] = Autocorr[1] / Autocorr[0];
AR_Coeff[1] = k[1];
// Initialize recursive criterion for order AR selection
if (AutoOrder == 1) {
FPE = AIC = MDL = CAT = CIC = Null;
CAT_factor = 0;
CIC_product = (1 + 1/(LongBar + 1))/(1 - 1/(LongBar + 1));
CIC_add = 1 + 1/(LongBar + 1);
}
// Main iterative loop
for (n = 1; n < OrderAR; n++) {
// Compute last coefficient
for (i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) AR_Coeff_inv[n+1-i] = AR_Coeff[i];
temp = 0;
for (i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) temp = temp + Autocorr[i] * AR_Coeff_inv[i];
beta[n+1] = Autocorr[n+1] - temp;
alpha[n+1] = alpha[n] * (1 - k[n]*k[n]);
k[n+1] = beta[n+1] / alpha[n+1];
AR_Coeff[n+1] = k[n+1];
// Compute other coefficients by recursion
for (i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) New_AR_Coeff[i] = AR_Coeff[i] - k[n+1] * AR_Coeff_inv[i];
New_AR_Coeff[n+1] = AR_Coeff[n+1];
// Update
AR_Coeff = New_AR_Coeff;
noise_variance[n+1] = alpha[n+1];
if (AutoOrder == 1) {
i = n + 1;
// Compute criterions for order AR selection
FPE[i] = noise_variance[i]*(LongBar + (i + 1))/(LongBar - (i + 1)); // Final Prediction Error
AIC[i] = log(noise_variance[i])+2*i/LongBar; // Akaine Information Criterion
MDL[i] = log(noise_variance[i]) + i*log(LongBar)/LongBar; // Minimum Description Length
CAT_factor = CAT_factor + (LongBar - i)/(LongBar*noise_variance[i]);
CAT[i] = CAT_factor/LongBar - (LongBar - i)/(LongBar*noise_variance[i]); // Criterion Autoregressive Transfer
CIC_product = CIC_product * (1 + 1/(LongBar + 1 - i))/(1 - 1/(LongBar + 1 - i));
CIC_add = CIC_add + (1 + 1/(LongBar + 1 - i));
CIC[i] = log(noise_variance[i]) + Max(CIC_product - 1,3*CIC_add); // Combined Information Criterion
}
// End main iterative loop
}
if (AutoOrder == 1) {
// Clean data because of rounding number for very low or very high value, and discard small changes
FPE = IIf(abs(LinRegSlope(FPE, 2)/FPE[1]) < 0.005 OR abs(FPE) > 1e7, Null, FPE);
AIC = IIf(log(abs(LinRegSlope(AIC, 2)/AIC[1])) < 0.005 OR abs(AIC) > 1e7, Null, AIC);
MDL = IIf(log(abs(LinRegSlope(MDL, 2)/MDL[1])) < 0.005 OR abs(MDL) > 1e7, Null, MDL);
CAT = IIf(log(abs(LinRegSlope(CAT, 2)/CAT[1])) < 0.005 OR abs(CAT) > 1e7, Null, CAT);
CIC = IIf(abs(LinRegSlope(CIC, 2)/CIC[1]) < 0.005 OR abs(CIC) > 1e7, Null, CIC);
// Find lower value
Mixed_Order = 0;
FPE_Order = Mixed_Order[1] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(FPE == Lowest(FPE) AND IsFinite(FPE), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
AIC_Order = Mixed_Order[2] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(AIC == Lowest(AIC) AND IsFinite(AIC), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
MDL_Order = Mixed_Order[3] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(MDL == Lowest(MDL) AND IsFinite(MDL), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
CAT_Order = Mixed_Order[4] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(CAT == Lowest(CAT) AND IsFinite(CAT), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
CIC_Order = Mixed_Order[5] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(CIC == Lowest(CIC) AND IsFinite(CIC), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
// Mixed array is an averaging from all criterions taking in consideration order choose by criterions is often too low
Mixed_Order_array = Median(Mixed_Order, 5); Mixed_Order = 2*ceil(Mixed_Order_array[5]);
// Print informations about best order for each criterion
printf("\nFPE Order : "+FPE_Order);
printf("\nAIC Order : "+AIC_Order);
printf("\nMDL Order : "+MDL_Order);
printf("\nCAT Order : "+CAT_Order);
printf("\nCIC Order : "+CIC_Order);
printf("\n*** Mixed Order *** : "+Mixed_Order);
// Mark best order in a[1] wich is returned at the end of the function
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "FPE") AR_Coeff[1] = FPE_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "AIC") AR_Coeff[1] = AIC_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "MDL") AR_Coeff[1] = MDL_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "CAT") AR_Coeff[1] = CAT_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "CIC (good)") AR_Coeff[1] = CIC_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "Mixed (best)") AR_Coeff[1] = Mixed_Order;
}
AR_Coeff[0] = alpha[OrderAR]; // noise variance estimator
return AR_Coeff;
}
function AR_YuleWalker(data, BegBar, EndBar, OrderAR, Biased, AutoOrder, AutoOrder_Criterion) {
BI = BarIndex();
Data_all = data;
Data = IIf(BI < BegBar, 0, IIf(BI > EndBar, 0, Data));
LongBar = EndBar - BegBar + 1;
// Window Hamming to make it more stable for non-biased estimator
if (Biased == 0) {
pi = atan(1) * 4;
x = Cum(1); x = Ref(x,-1); x[0] = 0;
W = 0.54 - 0.46*cos(2*pi*x/(LongBar-1));
Wi = Ref(W,-BegBar);
data = Wi*data;
}
// Compute Autocorrelation function
for (i = 0; i < OrderAR + 1; i++) {
temp = 0;
for (j = BegBar; j < EndBar + 1 - i; j++) {
temp = temp + data[j]*data[j+i];
}
if (Biased == 1) Autocorr[i]=(1/(LongBar))*temp; // biased estomator (best, model is always stable), small variance but less power
if (Biased == 0) Autocorr[i]=(1/(LongBar-i))*temp; // non-biased estimator (model can be unstable), large variance
}
Autocorr=Autocorr/Autocorr[0]; // normalization (don't change result, to be less exposed to bad rounding)
// Compute AR parameters with Durbin-Levison recursive algorithm for symmetric Toeplitz matrix (Hermitian matrix)
AR_Coeff = durbinlevison(Autocorr, OrderAR, LongBar, AutoOrder, AutoOrder_Criterion);
// End
AR_Coeff = IIf(BI > OrderAR, Null, AR_Coeff); // usefull for AR_Pred and AR_Freq
return AR_Coeff; // AR_Coeff[0] is noise variance estimator
}
function AR_Burg(data, BegBar, EndBar, OrderAR, Window, AutoOrder, AutoOrder_Criterion, DoublePrecision) {
BI = BarIndex();
LongBar = EndBar - BegBar + 1; // LongBar = the number of data
// Initialize recursive criterion for order AR selection
if (AutoOrder == 1) {
FPE = AIC = MDL = CAT = CIC = Null;
CAT_factor = 0;
CIC_product = (1 + 1/(LongBar + 1))/(1 - 1/(LongBar + 1));
CIC_add = 1 + 1/(LongBar + 1);
}
// Hamming window if selected
if (Window == 1) {
pi = atan(1) * 4;
x = Cum(1); x = Ref(x,-1); x[0] = 0;
W = 0.54 - 0.46*cos(2*pi*x/(LongBar-1));
}
// Create data, forward and backward coefficients arrays
y = Ref(data,BegBar); // y[0:LongBar-1] are the data
y = IIf(BI < LongBar, y, 0); // to be sure not to compute future data
f = b = y; // initialize forward and backward coefficients
// Initialize noise variance estimate with data variance (= data autocorrelation[0])
noise_variance = Cum(y^2);
noise_variance[0] = noise_variance[LongBar-1]/LongBar;
// Main loop
for (i = 1; i < OrderAR + 1; i++) {
if (Window == 1) Wi = Ref(W,-i); // center Hamming Window
else Wi = 1;
b_shifted = Ref(b,-1);
if (DoublePrecision == 0) { // single precision
k_temp = Sum(Wi*f*b_shifted, LongBar - i)/Sum(Wi*(f^2 + b_shifted^2), LongBar - i);
k[i] = 2*k_temp[LongBar - 1]; // k is reflection coefficient computed from i to LongBar - 1, like Burg tell it (!!! on Numerical Recipes it is computed from 1 to LongBar - i !!!)
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* --- PART JUST BELOW ARE ONLY FOR EXPERIMENTATION ABOUT ROUNDING PROBLEM, COMPUTATION IS SLOWER AND THIS IS NOT NEEDED FOR SMALL AR ORDER --- */
// Use for FOR loop instead SUM function give different result (neither good, neither bad, but just different) because of rounding single-precision in AFL. De-comment this part to use FOR loop.
/*
Num = 0;Den = 0;
for (j = i; j < LongBar; j++) { // compute from i to LongBar - 1, like Burg tell it (!!! on Numerical Recipes it is computed from 1 to LongBar - i !!!)
Num = Num + Wi[j]*( f[j]*b[j-1] );
Den = Den + Wi[j]*( f[j]^2 + b[j-1]^2 );
}
k[i] = 2*Num/Den; // k is reflection coefficient, a is AR coefficient
*/
/* --- END OF EXPERIMENTAL PART --- */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// If you wish Double Precision, VBS script must be used (result are more precise than SUM or FOR loop, but computation is a lot more slower)
if (DoublePrecision == 1) { // double precision
KI_VBS = GetScriptObject();
KI = KI_VBS.Compute_KI(f, b, Wi, i, LongBar);
k[i] = KI;
}
noise_variance[i] = (1 - k[i]^2)*noise_variance[i-1]; // update noise variance estimator
if (AutoOrder == 1) {
// Compute criterions for order AR selection
FPE[i] = noise_variance[i]*(LongBar + (i + 1))/(LongBar - (i + 1)); // Final Prediction Error
AIC[i] = log(noise_variance[i])+2*i/LongBar; // Akaine Information Criterion
MDL[i] = log(noise_variance[i]) + i*log(LongBar)/LongBar; // Minimum Description Length
CAT_factor = CAT_factor + (LongBar - i)/(LongBar*noise_variance[i]);
CAT[i] = CAT_factor/LongBar - (LongBar - i)/(LongBar*noise_variance[i]); // Criterion Autoregressive Transfer
CIC_product = CIC_product * (1 + 1/(LongBar + 1 - i))/(1 - 1/(LongBar + 1 - i));
CIC_add = CIC_add + (1 + 1/(LongBar + 1 - i));
CIC[i] = log(noise_variance[i]) + Max(CIC_product - 1,3*CIC_add); // Combined Information Criterion
}
// Update all AR coefficients
for (j = 1; j < i; j++) a[j] = a_old[j] - k[i]*a_old[i-j];
a[i] = k[i];
// Store them for next iteration
a_old = a;
// Update forward and backward reflection coefficients
f_temp = f - k[i]*b_shifted;
b = b_shifted - k[i]*f;
f = f_temp;
// End of the main loop
}
if (AutoOrder == 1) {
// Clean data because of rounding number for very low or very high value, and discard small changes
FPE = IIf(abs(LinRegSlope(FPE, 2)/FPE[1]) < 0.005 OR abs(FPE) > 1e7, Null, FPE);
AIC = IIf(log(abs(LinRegSlope(AIC, 2)/AIC[1])) < 0.005 OR abs(AIC) > 1e7, Null, AIC);
MDL = IIf(log(abs(LinRegSlope(MDL, 2)/MDL[1])) < 0.005 OR abs(MDL) > 1e7, Null, MDL);
CAT = IIf(log(abs(LinRegSlope(CAT, 2)/CAT[1])) < 0.005 OR abs(CAT) > 1e7, Null, CAT);
CIC = IIf(abs(LinRegSlope(CIC, 2)/CIC[1]) < 0.005 OR abs(CIC) > 1e7, Null, CIC);
// Find lower value
Mixed_Order = 0;
FPE_Order = Mixed_Order[1] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(FPE == Lowest(FPE) AND IsFinite(FPE), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
AIC_Order = Mixed_Order[2] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(AIC == Lowest(AIC) AND IsFinite(AIC), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
MDL_Order = Mixed_Order[3] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(MDL == Lowest(MDL) AND IsFinite(MDL), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
CAT_Order = Mixed_Order[4] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(CAT == Lowest(CAT) AND IsFinite(CAT), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
CIC_Order = Mixed_Order[5] = LastValue(Max(ValueWhen(CIC == Lowest(CIC) AND IsFinite(CIC), Cum(1), 1) - 1, 2));
// Mixed array is an averaging from all criterions taking in consideration order choose by criterions is often too low
Mixed_Order_array = Median(Mixed_Order, 5); Mixed_Order = 2*ceil(Mixed_Order_array[5]);
// Print informations about best order for each criterion
printf("\nFPE Order : "+FPE_Order);
printf("\nAIC Order : "+AIC_Order);
printf("\nMDL Order : "+MDL_Order);
printf("\nCAT Order : "+CAT_Order);
printf("\nCIC Order : "+CIC_Order);
printf("\n*** Mixed Order *** : "+Mixed_Order);
// Mark best order in a[1] wich is returned at the end of the function
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "FPE") a[1] = FPE_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "AIC") a[1] = AIC_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "MDL") a[1] = MDL_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "CAT") a[1] = CAT_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "CIC (good)") a[1] = CIC_Order;
if (AutoOrder_Criterion == "Mixed (best)") a[1] = Mixed_Order;
}
// End of the function, return AR coefficients and noise variance estimator for the current selected order in a[0]
a = IIf(BI > OrderAR, Null, a); a[0] = noise_variance[i-1]; // usefull for AR_Pred and AR_Freq
return a;
}
function AR_Predict(data, AR_Coeff, EndBar, ExtraF) {
BI = BarIndex();
OrderAR = LastValue(BarCount - BarsSince(AR_Coeff) - 1);
// Print some informations about AR coefficients and noise variance
sum_coeffs = Cum(AR_Coeff) - AR_Coeff[0]; // ARCoeff[0] store noise_variance
printf("\n\nNoise Variance Estimator : " + NumToStr(abs(AR_Coeff[0]), 1.9));
printf("\n\nSum of AR coeffs : " + NumToStr(sum_coeffs[OrderAR], 1.9));
for (i = 1; i < OrderAR + 1; i++) printf("\nCoeff AR " + NumToStr(i, 1.0) + " = " + NumToStr(AR_Coeff[i], 1.9));
// Pass the data into the AR filter
data_predict = IIf(BI > EndBar, Null, Data); // clear data after EndBar
for (i = Endbar + 1; i < EndBar + ExtraF + 1; i++) {
data_predict[i] = 0;
for (j = 1; j < OrderAR + 1; j++) data_predict[i] = data_predict[i] + AR_Coeff[j] * data_predict[i-j];
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* --- PART JUST BELOW IS ONLY IF YOU NEED RESIDUALS "u" FROM FILTERING PROCESS OR TO COMPARE IT WITH THE NOISE VARIANCE ESTIMATOR --- */
/*
global BegBar;
data_predict = IIf(BI > EndBar, Null, Data);
for (i = BegBar + OrderAR; i < EndBar + 1 + ExtraF; i++) {
data_predict[i] = 0;
for (j = 1; j < OrderAR + 1; j++) {
data_predict[i] = data_predict[i] + AR_Coeff[j] * data_predict[i-j];
}
if (i > EndBar) u[i] = 0; else u[i] = data[i] - data_predict[i];
data_predict[i] = data_predict[i] + u[i];
}
global noise_variance_filterburg;
noise_variance_filterburg = StDev(u, EndBar - (BegBar + OrderAR) + 1); noise_variance_filterburg = noise_variance_filterburg[EndBar]^2;
printf( "\n\nNoise variance from filtering process : " + NumToStr(noise_variance_filterburg, 1.9));
*/
/* --- END OF RESIDUAL COMPUTATION PART --- */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// Return data and data predicted from (EndBar + 1) to (EndBar + ExtraF)
return data_predict;
}
function AR_Freq(AR_Coeff, step) {
BI = BarIndex();
pi2 = atan(1) * 8;
OrderAR = LastValue(BarCount - BarsSince(AR_Coeff) - 1);
AR_Coeff=-AR_Coeff;
noise_variance = abs(AR_Coeff[0]);
if (noise_variance == 0) noise_variance = 0.000001; //seven-th digit to one
S = Null; // usefull to determine the number of data for AR_Sin function
f = Cum(1); f = Ref(f,-1); f[0] = 0; f = IIf(BI > 0.5/step, Null, f);
f = step*f;
// Danielson-Lanczos algorithm to fast compute exponential complex multiplication, using vector formulation AFL for multiple frequency in one-time recursion
W_cos = cos(pi2*f); W_sin = sin(pi2*f); // initialize cos and sinus constant for each frequency f
W_Re = 1; W_Im = 0; // initialize for recursion real and imaginary weight for AR coeffs
Re = 1; Im = 0; // initialize real and imaginary part of the denominator from the spectrum function
for (j = 1; j < OrderAR + 1; j++) {
W_Re_temp = W_Re; // Begin Danielson-Lanczos part
W_Re = W_Re*W_cos - W_Im*W_sin;
W_Im = W_Im*W_cos + W_Re_temp*W_sin; // End Danielson-Lanczos part
Re = Re + AR_Coeff[j]*W_Re; // real part of the denominator
Im = Im + AR_Coeff[j]*W_Im; // imaginary part of the denominator
}
/* Just for experimentation about speed between classic and Danielson-Lanczos algorithm, here is basic computation */
//Re = 1; Im = 0;
//for (j = 1; j < OrderAR + 1; j++) { Re = Re + AR_Coeff[j]*cos(pi2*f*j); Im = Im + AR_Coeff[j]*sin(pi2*f*j); }
S = noise_variance/(Re^2+Im^2); // S the spectrum function
Sdb = 10*log10(abs(s/noise_variance)); // Sdb the spectrum function in dB (power) with noise_variance as reference (so if Sdb is negative, power at this frequency is less than noise power)
return Sdb;
}
function AR_Sin(S, nb_sinus) {
// Initialization
nb_data = LastValue(BarCount - BarsSince(S));
step = 0.5/nb_data;
// Process data to keep only signifiant peaks
max_spectrum = Highest(S);
slope = LinRegSlope(S,2); // derivation
peaks = Ref(Cross(0, slope), 1); // find maximums of the spectrum
value_peaks = IIf(peaks == 1 AND S > 3 AND S / max_spectrum > 0.25, S, 0); // erase peaks only 3dB more from the noise or 75%dB less than the highest peak
// Find the reduced frequency of the most powerfull cycles
sinus = Null; sinus[0] = 0; // to detect error or no cycle
for (i = 0; i < nb_sinus; i++) { // save nb_sinus dominant cycles
sinus[i] = BarCount - LastValue(HighestBars(value_peaks)) - 1; // save higher peak position
value_peaks[sinus[i]] = 0; // erase new detected peak for next iteration
}
sinus = 1/(sinus*step); // convert reduced frequency in periods
sinus[0] = Nz(sinus[0]); // no cycle found
return sinus;
}
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* -------------------------------- DEMO -------------------------------- */
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// Choice of the parameters
empty = ParamList("Main parameters", "", 0);
data_source = ParamField("Price field",-1);
ARmodel = ParamList("AR Model", "Burg (best)|Yule-Walker", 0);
length = Param("Length to look back", 200, 1, 5000, 1);
OrderAR = Param("Order AR", 20, 0, 100, 1);
ExtraF = Param("Number of bar to predict", 50, 0, 200, 1);
AutoOrder = ParamToggle("Auto AR order", "No|Yes", 0);
AutoOrder_Criterion = ParamList("Auto AR criterion", "FPE|AIC|MDL|CAT|CIC (good)|Mixed (best)", 5);
HammingWindow = ParamToggle("Burg: Hamming Window", "No|Yes", 1);
DoublePrecision = ParamToggle("Burg: Double Precision", "No|Yes", 0);
Biased = ParamToggle("Y-W: Biased (Yes: best)", "No|Yes", 1);
empty = ParamList("*** PRE-PROCESSING : ***", "", 0);
empty = ParamList("1- Intraday EOD GAP Filter", "", 0);
FiltrageGAPEOD = ParamToggle("Filtrage GAP EOD", "No|Yes", 0);
empty = ParamList("2- Denoise", "", 0);
periodsT3 = Param("Periods T3", 1, 1, 200, 1);
slopeT3 = Param("Slope T3", 0.7, 0, 3, 0.01);
empty = ParamList("3- Detrend", "", 0);
method_detrend = ParamList("Detrending method", "None|Log10|Derivation|Linear Regression|PolyFit", 3);
PF_order = Param("PolyFit Order", 3, 1, 9, 1);
empty = ParamList("4- Center", "", 0);
PreCenter = ParamToggle("Center data", "No|Yes", 1);
empty = ParamList("5- Normalize", "", 0);
PreNormalise = ParamToggle("Normalise data", "No|Yes", 1);
empty = ParamList("6- Volume weight on data", "", 0);
PonderVolHL = ParamToggle("Weighting Volume and H/L(Fractal)", "No|Yes", 0);
coef_vol = Param( "Strength Volume (- +)", 0.5, 0.01, 0.99, 0.01);
coefdim = Param( "Strength Fractal (- +)", 0.5, 0.01, 0.99, 0.01);
period = Param( "Periods Fract (even)", 16, 2, 200, 2);
scale = Param( "Scale Final Weights", 1, 0, 10, 0.01);
translation = Param( "Translate Final Weights", 0.3, 0, 1, 0.01);
empty = ParamList("7- Time weight on data", "", 0);
PonderTime = ParamToggle("Weighting Time", "No|Yes", 0);
PonderTimeWindow = ParamList("Weighting Time Window", "Log|Ramp|Exp", 0);
empty = ParamList("*** POST-PROCESSING : ***", "", 0);
method_retrend = ParamList("Retrending method", "Add back trend|Prediction without trend", 0);
empty = ParamList("For Derivation or Log10 :", "add automatically the trend", 0);
// Initialization
SetBarsRequired(20000,20000);
Title = "";
BI = BarIndex();
current_pos = SelectedValue( BI ) - BI[ 0 ];//1500
printf( "Position: " + NumToStr(current_pos) + "\n" );
// Adjust users choice depending number of bars data available or detrending/retrending necessity for derivation method
if ( method_retrend == "Prediction without trend" AND (method_detrend == "Derivation" OR method_detrend == "Log10") ) method_retrend = "Add back trend";
BegBar = current_pos - length + 1;
slide = floor(periodsT3/2);
if (BegBar < 6*periodsT3) Title = Title + "\n\n\n\n\n\n!!! WARNING : YOU HAVE NOT ENOUGH DATA HISTORY FOR CORRECT T3 FILTERING - Reduce \"Periods T3\" parameter OR move Position Bar !!!\n\n\n\n\n\n";
if (BegBar < 1) {
BegBar = 1;
length = current_pos - slide;
Title = Title + "\n\n\n\n\n\n!!! WARNING : YOU HAVE NOT ENOUGH DATA HISTORY - Reduce \"Length to look back\" parameter OR move Position Bar !!!\n\n\n\n\n\n";
}
EndBar = current_pos - slide;
if ( EndBar + ExtraF > BarCount - 1) {
ExtraF = (BarCount - 1) - EndBar;
}
if (AutoOrder == 1) OrderAR = floor(length / 2);
if (OrderAR >= length) {
OrderAR = length - 1;
Title = Title + "\n\n\n\n\n\n!!! WARNING : ORDER AR IS MORE HIGH THAN (LENGTH TO LOOK BACK - 1) - Reduce \"Order AR\" OR increase \"Length to look back\" parameters !!!\n\n\n\n\n\n";
}
data = data_source;
data_filtred = f_centeredT3(data, periodsT3, slopeT3);
/* -------------------- BEGIN PROCESSING -------------------- */
// Filter GAP End of the days - only needed for intraday
if (FiltrageGAPEOD == 1) data = Filter_GAP_EOD(data);
// Denoise data
data = f_centeredT3(data, periodsT3, slopeT3);
// Detrend data
if (method_detrend != "None") data = f_detrend(data, BegBar, EndBar, ExtraF, method_detrend, PF_order);
data = IIf(BI < BegBar, 0, data); // fill with 0 before BegBar to be able to compute native MA Function AFL
// Center data
mean_data_before = MA(data, EndBar - BegBar + 1);
printf( "\nMean data not centered : " + WriteVal(mean_data_before[EndBar]) + "\n" );
if (PreCenter == 1) {
data = data - mean_data_before[EndBar];
mean_data_after = MA(data, EndBar - BegBar + 1);
printf( "\nMean data centered : " + WriteVal(mean_data_after[EndBar]) + "\n\n" );
}
// Normalize data
if (PreNormalise == 1) {
max_data = HHV(data, EndBar - BegBar + 1);
data = data / max_data[EndBar];
}
// Weigthing only for the data which will feed the AR_Burg function (modeling AR), not the AR_Pred function (prediction)
data_weighted = data;
// Volume and High/Low (Fractal) weighting
if (PonderVolHL == 1) data_weighted = Volume_HighLow_weighting(data_weighted, coef_vol, coefdim, period, scale, translation);
// Time weighting
if (PonderTime == 1) data_weighted = Time_weighting(data_weighted, PonderTimeWindow, BegBar, EndBar);
// Compute AR model
if (ARmodel == "Burg (best)") { // Burg model (MEM method) (better than Yule-Walker for sharp spectrum and short data history)
AR_Coeff = AR_Burg(data_weighted, BegBar, EndBar, OrderAR, HammingWindow, AutoOrder, AutoOrder_Criterion, DoublePrecision);
if (AutoOrder == 1) { // In case of AutoOrder, a new computation to find coefficients with the ideal order is needed
OrderAR = AR_Coeff[1];
AR_Coeff = AR_Burg(data_weighted, BegBar, EndBar, OrderAR, HammingWindow, 0, AutoOrder_Criterion, DoublePrecision); // Compute the AR from AutoOrder
}
}
if (ARmodel == "Yule-Walker") { // Yule-Walker model (Autocorrelation method)
AR_Coeff = AR_YuleWalker(data_weighted, BegBar, EndBar, OrderAR, Biased, AutoOrder, AutoOrder_Criterion);
if (AutoOrder == 1) { // In case of AutoOrder, a new computation to find coefficients with the ideal order is needed
OrderAR = AR_Coeff[1];
AR_Coeff = AR_YuleWalker(data_weighted, BegBar, EndBar, OrderAR, Biased, 0, AutoOrder_Criterion); // Compute the AR from AutoOrder
}
}
noise_variance = abs(AR_Coeff[0]);
// Prediction based on the computed AR model (not necessary for TrigFit)
//data_predict = AR_Predict(data, AR_Coeff, EndBar, ExtraF);
// Compute spectrum based directly on AR model. Decomment following line to plot spectrum begining in first Bar (Bar[0])
Sdb = AR_Freq(AR_Coeff, 0.001); // 0.001 is the step for frequency resolution
//Plot( Sdb, "Spectrum in decibels", ParamColor( "Color Spectrum in decibels", colorCycle ), ParamStyle("Style") );
// Look for the frequency which are the more powerfull (dominant cycles)
sinus = AR_Sin(Sdb, 10); // 10 is the maximum number of frequency to look for
// Compute Amplitudes and Phases
nb_sinus = LastValue(BarCount - BarsSince(IsFinite(sinus)));
if (sinus[0] == 0) nb_sinus = 0;
AP_VBS = GetScriptObject();
amplitudesphases = AP_VBS.TrigFit_amplitudesphases(data, BegBar, EndBar, sinus, nb_sinus);
for (i=1;i<=2*nb_sinus;i=i+2) {
amplitudes[(i+1)/2 - 1] = amplitudesphases[i];
phases[(i+1)/2 - 1] = amplitudesphases[i+1];
}
data_predict = 0;
pi = atan(1) * 4;
for (i=0; i < nb_sinus; i++) {
data_predict = data_predict + amplitudes[i]*sin(2*pi*BI/sinus[i] + phases[i]);
}
for (i=0; i < nb_sinus; i++) { // Print some informations about Periods, Amplitudes and Phases for the main cycles
printf("Cycle"+i+"(t) = "+amplitudes[i]+"*sin(2*pi*t/"+sinus[i]+" + "+phases[i]+")\n");
}
// De-normalize
if (PreNormalise == 1) {
data_predict = data_predict * max_data[EndBar];
noise_variance = noise_variance * max_data[EndBar];
}
// De-center
if (PreCenter == 1) data_predict = data_predict + mean_data_before[EndBar];
// Add the trend back again
if (method_detrend != "None" AND method_retrend == "Add back trend") data_predict = f_retrend(data_predict, data_filtred[BegBar], BegBar, EndBar + ExtraF, method_detrend);
// Translate along value axis filtered EOD GAP data or not retrended data, so no gap occurs
if (FiltrageGAPEOD == 1 OR (method_detrend != "None" AND method_retrend == "Prediction without trend")) {
delta = data_predict[EndBar + 1] - data_filtred[EndBar];
data_predict = data_predict - delta;
data_predict = Ref(data_predict, 1); // so there is no discontinuity (but there is one data less for forward prediction)
}
// Plot AR Prediction and Burg predicted channels based on ATR and noise variance (if prediction is bad, channel will be larger)
//dataATR = ATR(periodsT3); // no need to detrend or center ATR before prediction (considerer centred without any trend)
//printf("\n\nATR AR model for Channel prediction :\n");
//AR_Coeff_ATR = AR_Burg(dataATR, BegBar, EndBar, OrderAR, HammingWindow, OrderAR, AutoOrder_Criterion, DoublePrecision);
//data_predict_ATR = AR_Predict(dataATR, AR_Coeff_ATR, EndBar, ExtraF);
//DeltaBand = 2*(data_predict_ATR + noise_variance);
Data_reconstruct = Null;
Data_reconstruct = IIf( BI <= EndBar AND BI >= BegBar, data_predict, IIf( BI > EndBar AND BI <= EndBar + ExtraF, data_predict, Data_reconstruct));
Plot(Data_reconstruct, "AR("+ NumToStr(OrderAR, 1.0) +") Prediction", IIf(BI > EndBar + slide, colorRed, IIf(BI > EndBar AND BI <= EndBar + slide, colorBlue, colorBrightGreen)), styleThick, Null, Null, 0);
//Plot(Data_reconstruct + DeltaBand, "AR("+ NumToStr(OrderAR, 1.0) +") Prediction Upper Channel", IIf(BI > EndBar + slide, colorRed, IIf(BI > EndBar AND BI <= EndBar + slide, colorBlue, colorBrightGreen)), styleDashed, Null, Null, 0);
//Plot(Data_reconstruct - DeltaBand, "AR("+ NumToStr(OrderAR, 1.0) +") Prediction Lower Channel", IIf(BI > EndBar + slide, colorRed, IIf(BI > EndBar AND BI <= EndBar + slide, colorBlue, colorBrightGreen)), styleDashed, Null, Null, 0);
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* ------------------------------- END DEMO ----------------------------- */
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------- */
3 comments
Leave Comment
Please login here to leave a comment.
Back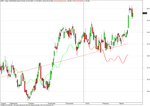
Thanks. You can check also “AR Prediction” code within Wisestocktrader.com’s database, which is slightly different.
Regards,
thk.
error